
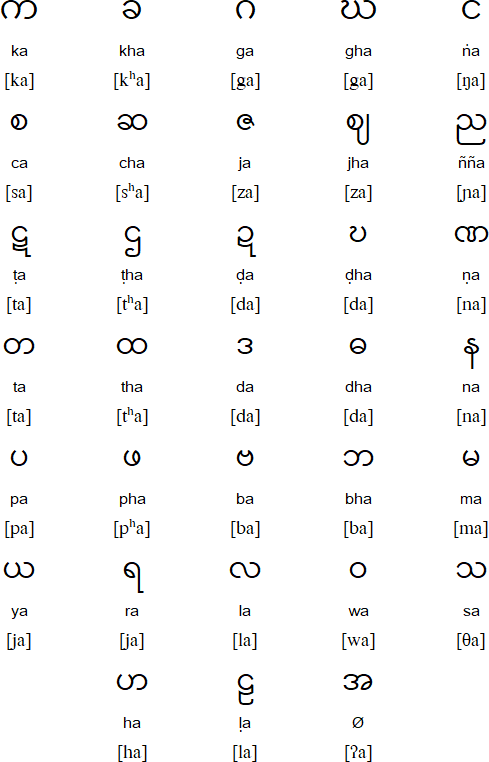

The language is widely used on the internet as well. Since the Burmese government lifted censorship in 2012, Burmese publications have constantly expanded. Despite the country’s censorship system, which lasted half a century, Myanmar saw vigorous publishing activities, covering genres from novels to cartoons. It has a long history of use in traditional literary works and music. Burmese is also the main lingua-franca in the country as well as in Burmese communities worldwide. Linguistic map of Burma from Muturzikin.Burmese is the official language of Myanmar, which has a population of 54 million, where around 70% are mother-tongue speakers of the language.Thein, Myat (2004), Economic Development of Myanmar, Institute of Southeast Asian Studies, ISBN 981-230-211-5.

Lintner, Bertil (2003), "Myanmar/Burma", in MacKerras, Colin (ed.), Ethnicity in Asia, Routledge, ISBN 6-2.(2015), Ethnologue: Languages of the World (18 ed.), SIL International, retrieved 4 April 2015 Goddard, Cliff (2005), The Languages Of East And Southeast Asia: An Introduction, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-924860-5.Lavras, MG, Brazil: University of Lavras. Revista InforComp (INFOCOMP Journal of Computer Science). "First Classified Annotated Bibliography of NLP Tasks in the Burmese Language of Myanmar". It is not clear if there are one or two Burmese sign languages. In Myanmar, usage of its minority languages is discouraged. Most of these languages use the Myanmar (Burmese) script. Indigenous languages Īside from Myanmar (Burmese) and its dialects, the hundred or so languages of Myanmar include Shan (Tai, spoken by 3.2 million), Karen languages (spoken by 2.6 million), Kachin (spoken by 900,000), Thamizh (spoken by 1.1 Million), various Chin languages (spoken by 780,000), and Mon (Mon–Khmer, spoken by 750,000). The scope for further research too has been explored for areas of parallel corpus development as well as development of search engine and WordNet for the Burmese language. Īs far as natural language processing research dealing with interaction of computers and Burmese human-spoken language is concerned, during the period spanning more than 25 years, from 1990 to 2016, notable work has been done and annotated in the areas of Burmese language word identification, segmentation, disambiguation, collation, semantic parsing and tokenization followed by part-of-speech tagging, machine translation systems, text keying/input, text recognition and text display methods. Burmese was the fourth of the Sino-Tibetan languages to develop a writing system, after Chinese, Tibetan, and Tangut. Burmese is the most widely spoken of the Tibeto-Burman languages and among the Sino-Tibetan languages, the second most widely spoken, after the Sinitic languages. īurmese is a Sino-Tibetan language belonging to the Southern Burmish branch of the Tibeto-Burman languages. Burmese is spoken as a second language by another 10 million people, particularly ethnic minorities in Burma and those in neighbouring countries. In 2007, Burmese was spoken by 33 million people as a first language. Burmese is the native language of the Bamar people and related sub-ethnic groups of the Bamar, as well as that of some ethnic minorities in Burma like the Mon.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
